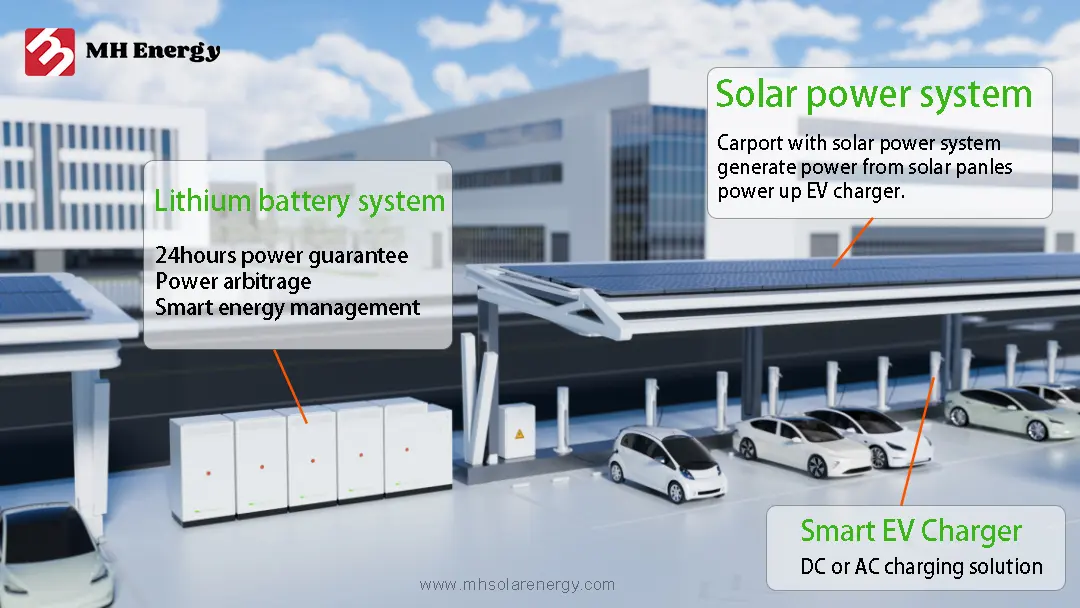
3 things you should to konw about Hybrid inverter and Off grid inverter
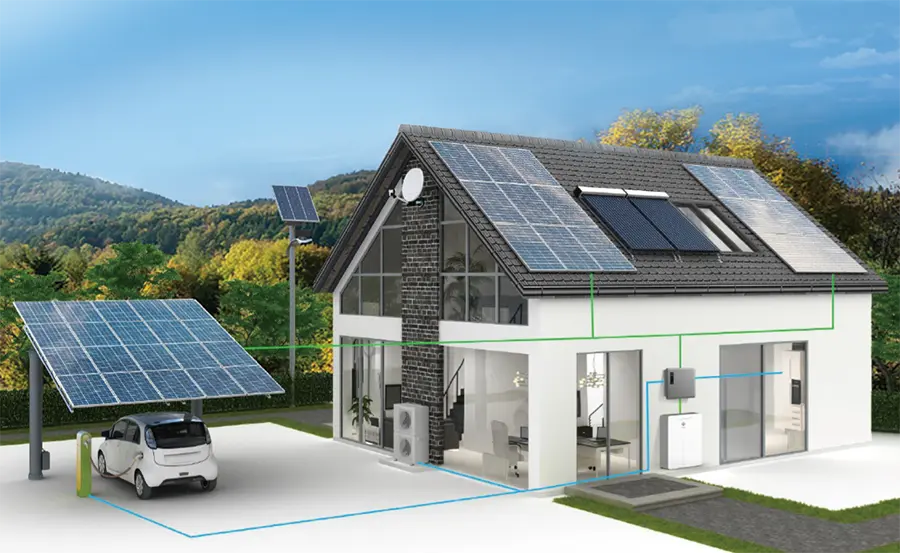
Amid the rapid development of Renewable Energy, energy storage inverters play a critical role as the key component connecting renewable energy systems to the grid or loads. Among them, off-grid and hybrid energy storage inverters have gained significant attention due to their distinct operating modes and application scenarios. This article provides a brief overview of the basic principles behind these two types of inverters and highlights their key differences.
01 Key Features
Off-Grid Energy Storage Inverters
Primarily convert the direct current (DC) generated by Solar Panels into alternating current (AC) to power electrical loads.
Usually paired with energy storage batteries to store excess electricity and release it when needed.
Operate independently of the grid, making them suitable for remote or off-grid areas.

Hybrid Energy Storage Inverters
Combine both off-grid and grid-tied functionalities: they can convert solar-generated DC into AC for load use and also connect to the grid for bidirectional power flow.
When the grid is available, they can draw electricity from it to supplement solar generation; during grid outages, they automatically switch to off-grid mode to continue powering loads.
Feature high-efficiency inversion and intelligent charging capabilities, adjusting charging parameters based on battery status to extend battery lifespan.

02 Application Scenarios
Off-Grid Energy Storage
Primarily used in remote mountains, deserts, islands, or other regions without grid access or with unstable power supply.
Suitable for residential use, small-scale commercial projects, or any situation requiring independent power supply.
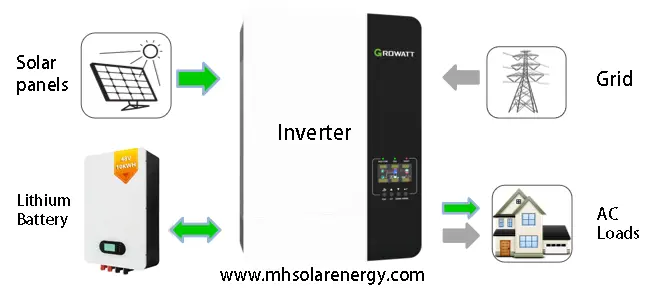
Hybrid Energy Storage
Ideal for areas with grid access where users aim to reduce electricity bills or achieve energy self-sufficiency through Solar Power.
Widely applicable to homes, businesses, and public facilities—especially in regions with an unstable grid or where improving energy efficiency is a priority.
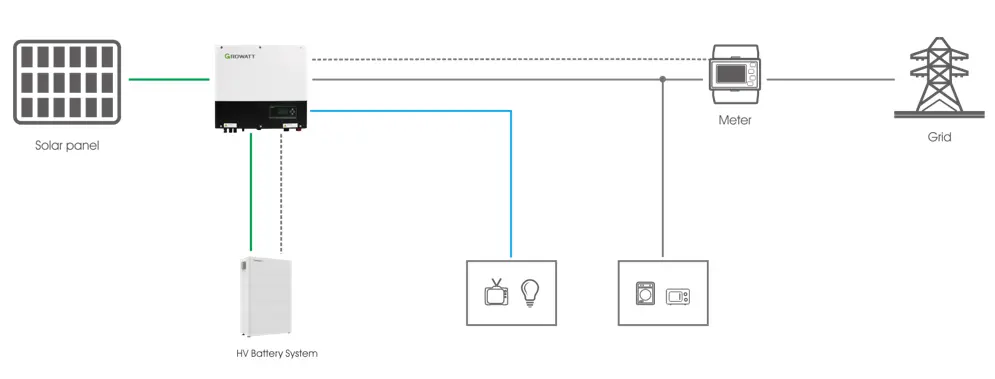
03 Key Differences
| Category | Off-Grid Energy Storage | Hybrid Energy Storage |
| Operating Mode | Stores electricity from solar generation or excess grid power in batteries; converts battery DC into AC when needed. | Automatically switches between grid-tied and off-grid modes based on grid status. Feeds excess renewable energy back to the grid when connected; uses stored battery power during outages. |
| Application Scope | Suitable for remote areas, islands, and mobile/nomadic setups without stable grid power. | Suitable for larger renewable energy power stations, microgrids, or sites requiring both grid-connected and off-grid functionalities. |
| Protection Rating | Typically installed indoors with lower protection requirements (commonly IP20). Usually installed outdoors or on rooftops, requiring higher protection ratings (typically IP65 or above). System Complexity Relatively simple, focused on self-sufficiency. | More complex, with advanced features and control strategies designed to adapt to dynamic power environments. |
| Cost & Lifespan | Lower in cost due to simpler design; suitable for basic needs. | Higher in cost due to greater complexity, but offers better energy efficiency and system stability over time. |
Off-grid and hybrid energy storage inverters each have their own advantages and suitable use cases. When selecting between the two, users should carefully evaluate their actual power needs, budget constraints, and specific application scenarios to determine the most appropriate solution. Contact us now of the suitable solution for your projects.