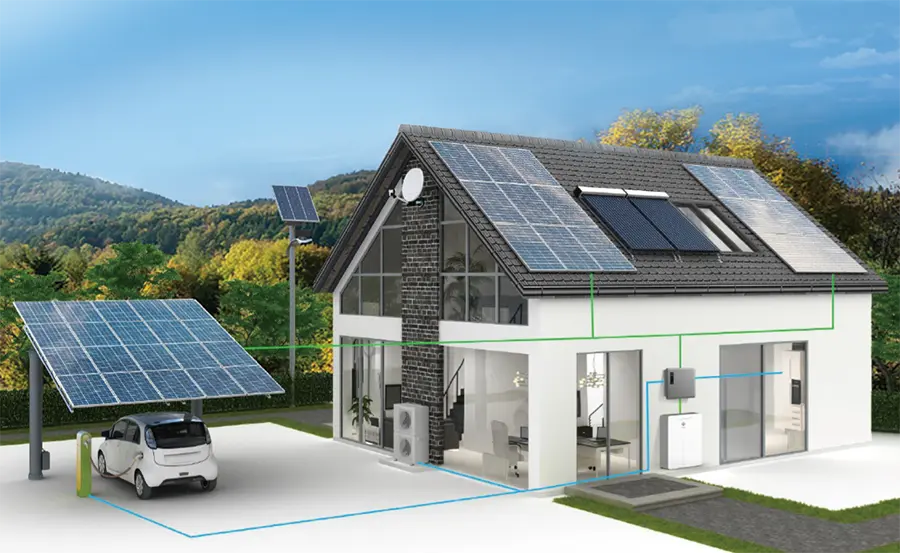
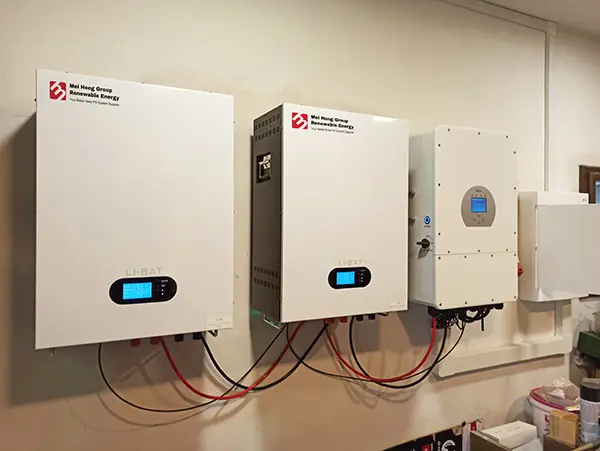
Maximizing Solar Power: Essential Maintenance & Troubleshooting for PV Stations
Maximizing Solar Power: Essential Maintenance & Troubleshooting for PV Stations
Efficient operation and maintenance (O&M) of photovoltaic (PV) Power Stations are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and long-term reliability. To quickly and effectively troubleshoot power stations, here are essential routine precautions, fault prediction methods, and troubleshooting techniques.
1. Initial Inspection: Identifying AC or DC Faults
The first step in diagnosing a PV power station issue is checking the inverter display for error prompts. This helps determine whether the fault is on the AC or DC side.
1.1 AC Faults and Troubleshooting
Common AC faults include:
- Utility power outage – Verify grid power availability.
- Loose connections in the electricity meter or air switch – Often caused by thermal expansion and contraction; inspect and tighten connections.
- Incorrect selection of air switch or leakage protector – Ensure compatibility with the system’s power specifications.
- Quality issues with air switch or leakage protector – Check for faulty copper pressure plates; use a multimeter for testing while maintaining safety protocols.
- Live and neutral wires reversed – Causes phase sequence issues preventing proper operation.
- Grounding issues due to wire sheath wear – Inspect and replace damaged insulation.
- Neutral and ground wires reversed – Leads to frequent tripping and leakage issues.
- Loose grid connection clamps – Inspect and tighten high-voltage connections every two years.
Troubleshooting Tip: Use on-site visual inspections and a multimeter to locate AC issues efficiently. Always use one hand when switching on or off and keep your face away from the electrical box to prevent arc burns.
1.2 DC Faults and Troubleshooting
Common DC faults include:
- Insufficient module voltage – Inverters operate within 100V–900V; below 100V, the system won’t function. Causes may include string leakage or defective modules.
- Reverse polarity connections – PV terminals have specific positive and negative orientations; mismatching them can lead to faults.
- DC line wear and low insulation resistance – DC lines must be properly sleeved to prevent deterioration.
- Incorrect MC4 connector pairing – Male and female connectors must be correctly matched to ensure proper current flow.
- Improper DC line connections – Directly connecting DC lines without an MC4 connector can lead to sparking, overheating, and potential fire hazards.
- Communication rod connection issues – If the connection is faulty, data transmission may be interrupted.
- Inverter overheating – Units installed too close to a wall (less than 30 cm) may overheat and shut down.
- Poor DC cable management – Long-term exposure to wind can cause wire damage, leading to grounding faults.
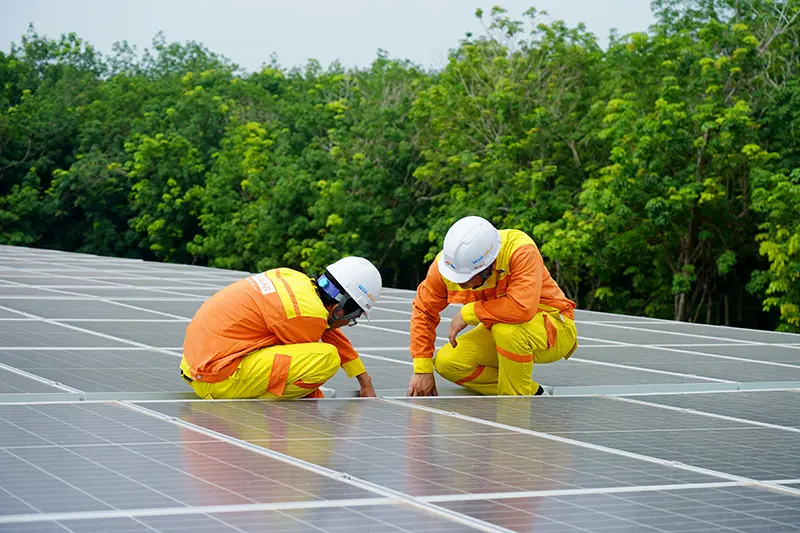

2. Preventative Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Routine maintenance is essential to prevent unexpected failures and enhance system efficiency. Key maintenance practices include:
- Regular inspections – Check for loose connections, worn cables, and corrosion.
- Cleaning modules – Remove dust, dirt, bird droppings, and other obstructions to maintain maximum efficiency.
- Vegetation control – Trim weeds, vines, and other plants that may shade panels or interfere with wiring.
- Monitoring system performance – Use remote monitoring tools to track system efficiency and detect early warning signs of failure.
- Checking environmental factors – Ensure that shading from newly constructed buildings or growing trees does not impact energy production.
By implementing these troubleshooting and maintenance best practices, PV power station operators can maximize energy output, reduce downtime, and enhance the system’s longevity. Regular monitoring, inspections, and preventive actions are key to a well-functioning solar power station.
For professional maintenance services and high-quality solar energy solutions, feel free to contact us now.