Solar Power System 101: A Comprehensive Guide
As the world pivots toward sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a leading contender in the Renewable Energy sector. Understanding the fundamentals of a solar power system is crucial for anyone considering this clean, efficient, and cost-effective energy source. This guide will provide you with an overview of solar power systems, the configuration components, types, and benefits.
What is a Solar Power System?
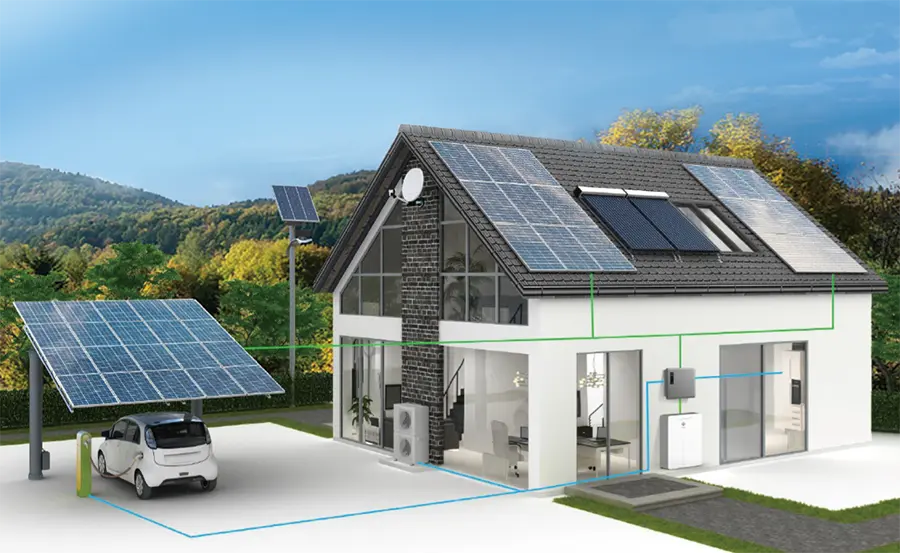
A solar power system harnesses energy from the sun and converts it into electricity to power homes, businesses, and other facilities. The system consists of several key components that work together to capture, convert, and distribute Solar Energy.
Key Components of a Solar Power System
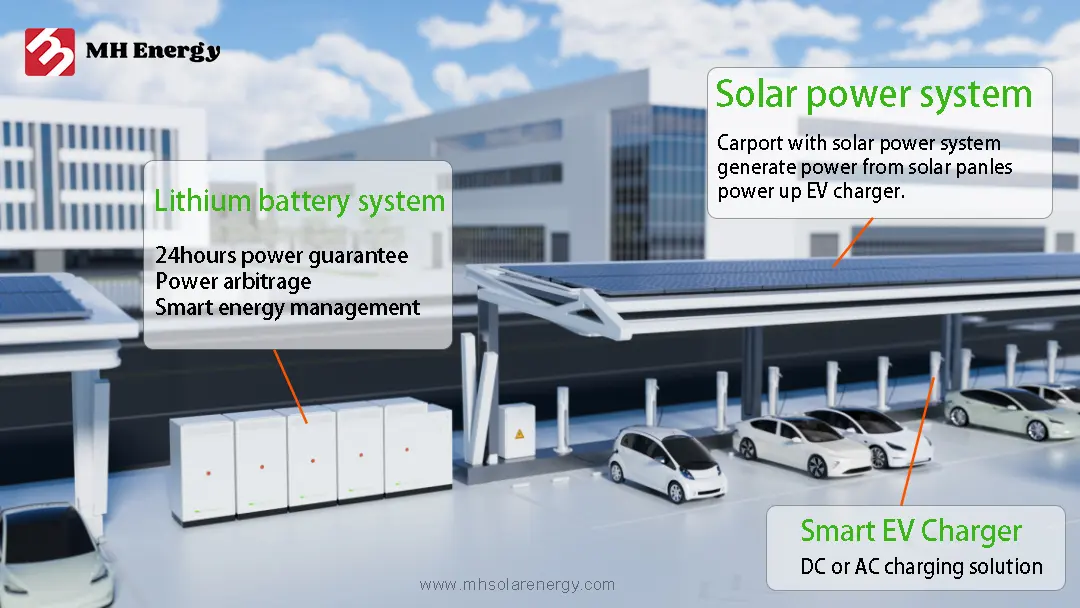
1. Solar Panels: These are the most visible components of a solar power system. Made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells(solar cells), solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
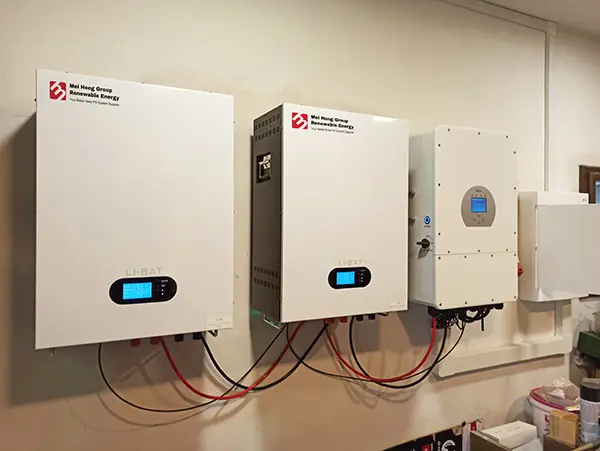
2. Inverter: Since most household appliances run on alternating current (AC) electricity, the inverter’s role is to convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into AC electricity. There are different types of inverters, including string inverters, microinverters, and hybrid inverters.
3. Mounting System: This hardware supports the solar panels, securing them to rooftops or other structures. The mounting system must be robust enough to withstand various weather conditions, they are galvanized or aluminium alloy with accessories.
4. Battery Storage: For systems that store energy for later use, such as during the night or on cloudy days, batteries are essential. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used due to their efficiency and long lifespan. There are Low voltage and High voltage lithium battery for your system.
5. Charge Controller: This device regulates the voltage and current coming from the solar panels to the batteries, ensuring they charge safely without overloading.
6. Grid Connection: In grid-tied systems, excess energy can be fed back into the local utility grid, potentially earning the system owner credits or payments through net metering.

Types of Solar Power Systems
1. On-Grid Systems: These systems are connected to the local utility grid. They do not include battery storage but allow homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid. This setup is cost-effective and widely used in urban areas.
2. Off-Grid Systems: These systems operate independently from the local utility grid and typically include battery storage to provide power during non-sunny periods. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote areas where grid access is unavailable or unreliable.
3. Hybrid Systems: Combining features of both on-grid and off-grid systems, hybrid systems are connected to the grid but also include battery storage. This allows for greater energy independence and reliability.
Benefits of Solar Power Systems
1. Cost Savings: By generating your own electricity, you can significantly reduce your utility bills. In many regions, government incentives and tax credits further offset the initial investment costs.
2. Environmental Impact: Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
3. Energy Independence: With a solar power system, you are less reliant on external energy providers, which can be particularly advantageous during power outages or energy price spikes.
4. Increased Property Value: Homes equipped with solar power systems often see an increase in property value, as potential buyers are attracted to the energy savings and sustainability features.
Understanding the basics of solar power systems is the first step toward harnessing the sun’s energy to power your home or business. With various system types and components available, solar power offers a versatile and sustainable solution for reducing energy costs and environmental impact. Whether you opt for an on-grid, off-grid, or hybrid system, investing in solar power is a step toward a brighter, greener future.